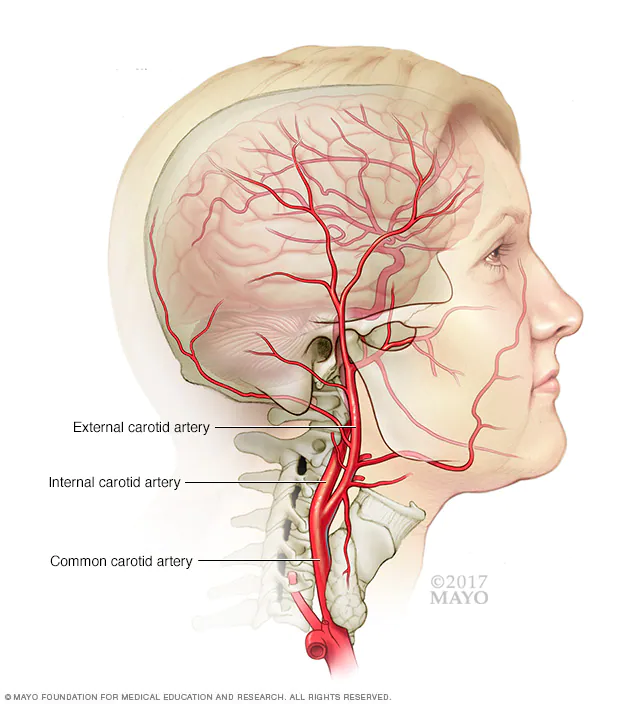
Carotid artery disease occurs when the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This narrowing restricts blood flow to the brain and increases the risk of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), also known as a mini-stroke.
The condition is often associated with risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes. Symptoms may include weakness or numbness on one side of the body, trouble speaking or understanding speech, and sudden dizziness or loss of balance.
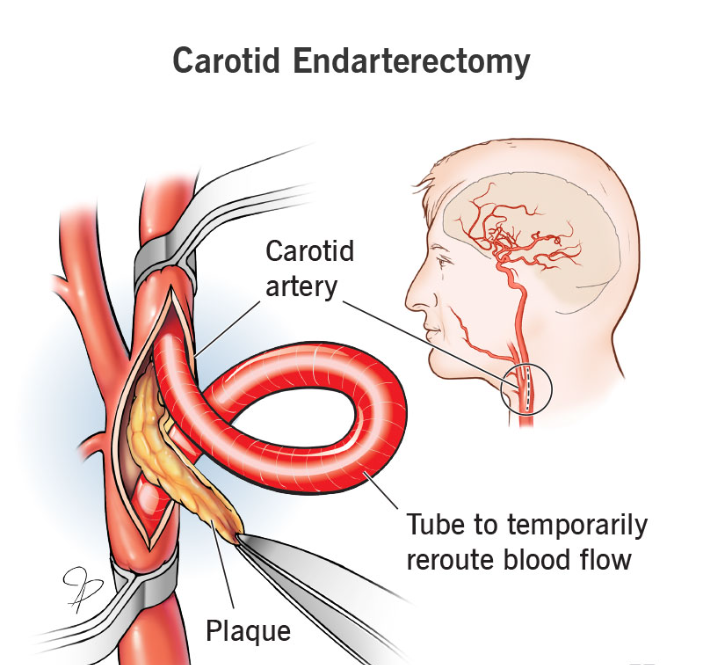
Management of carotid artery disease involves lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, exercise, and medication to control risk factors. In some cases, carotid artery surgery or procedures like carotid artery stenting may be recommended to restore proper blood flow and reduce the risk of stroke.